Autonomous Locomotion Mode Transition Simulation of a Track-legged Quadruped Robot Step Negotiation
Published in arXiv:1905.04235, 2019
Abstract
Multi-modal locomotion (e.g. terrestrial, aerial, and aquatic) is gaining increasing interest in robotics research as it improves the robots’ environmental adaptability, locomotion versatility, and operational flexibility. Within the terrestrial multiple locomotion robots, the advantage of hybrid robots stems from their multiple (two or more) locomotion modes, among which robots can select from depending on the encountering terrain conditions. However, there are many challenges in improving the autonomy of the locomotion mode transition between their multiple locomotion modes.
This work proposed a method to realize an autonomous locomotion mode transition of a tracklegged quadruped robot’s steps negotiation. The autonomy of the decision-making process was realized by the proposed criterion to comparing energy performances of the rolling and walking locomotion modes. Two climbing gaits were proposed to achieve smooth steps negotiation behaviours for the energy evaluation purposes. Simulations showed autonomous locomotion mode transitions were realized for negotiations of steps with different height. The proposed method is generic enough to be utilized to other hybrid robots after some pre-studies of their locomotion’s energy performances.
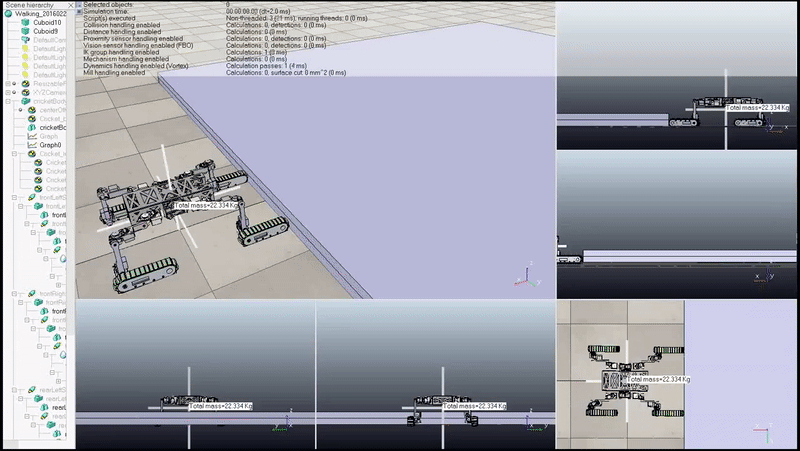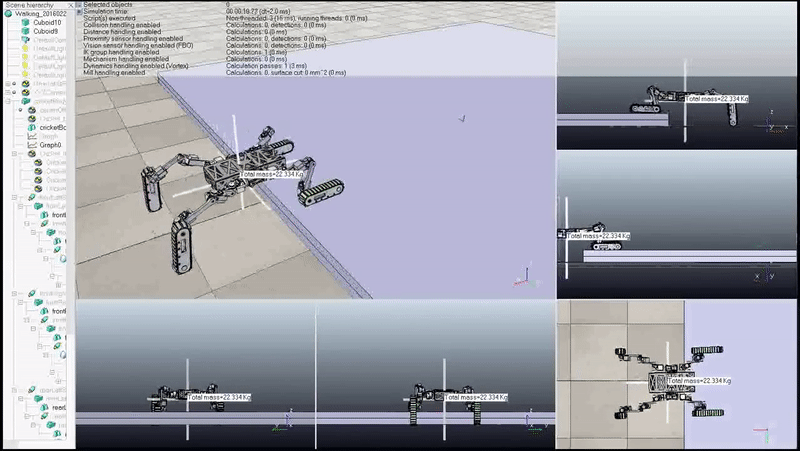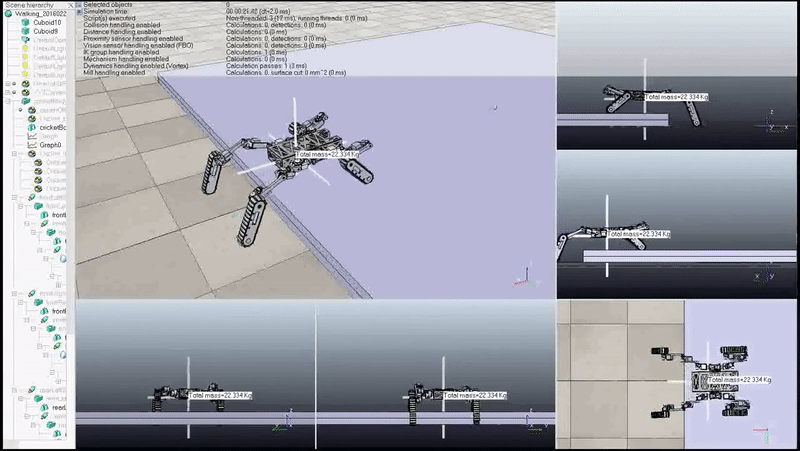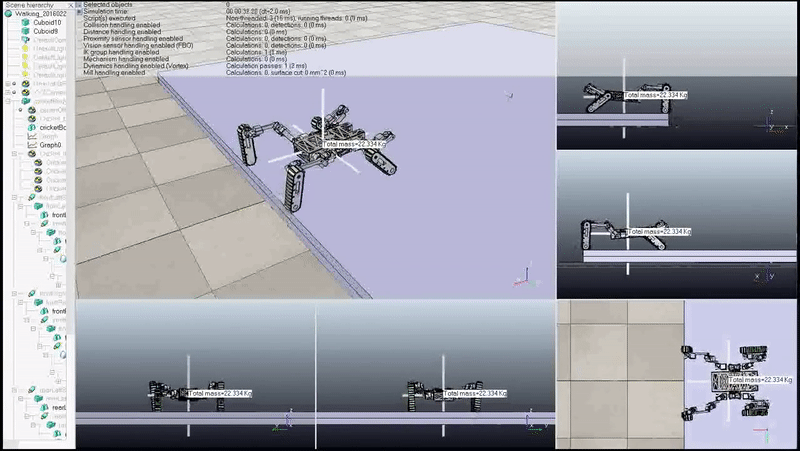
Full Body Step Negotiation Gait:
Locomotion Mode Transition: